纪念一下本辣鸡在hdu刷的第100道水题,
比较标准的dfs..
Red and Black
Problem Description
There is a rectangular room, covered with square tiles. Each tile is colored either red or black. A man is standing on a black tile. From a tile, he can move to one of four adjacent tiles. But he can’t move on red tiles, he can move only on black tiles.
Write a program to count the number of black tiles which he can reach by repeating the moves described above.
Input
The input consists of multiple data sets. A data set starts with a line containing two positive integers W and H; W and H are the numbers of tiles in the x- and y- directions, respectively. W and H are not more than 20.
There are H more lines in the data set, each of which includes W characters. Each character represents the color of a tile as follows.
‘.’ – a black tile
‘#’ – a red tile
‘@’ – a man on a black tile(appears exactly once in a data set)
Output
For each data set, your program should output a line which contains the number of tiles he can reach from the initial tile (including itself).
Sample Input
6 9
….#.
…..#
……
……
……
……
……
#@…#
.#..#.
11 9
.#………
.#.#######.
.#.#…..#.
.#.#.###.#.
.#.#..@#.#.
.#.#####.#.
.#…….#.
.#########.
………..
11 6
..#..#..#..
..#..#..#..
..#..#..###
..#..#..#@.
..#..#..#..
..#..#..#..
7 7
..#.#..
..#.#..
###.###
…@…
###.###
..#.#..
..#.#..
0 0
Sample Output
45
59
6
13
代码实现
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Dfs1312 {
public static char a[][];
public static int book[][];
public static int l;
public static int h;
public static int sum;
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
while (in.hasNext()) {
l = in.nextInt();
h = in.nextInt();
if (h == 0 && l == 0) {
break;
}
a = new char[h][l];
int startx = 0;
int starty = 0;
book = new int[h][l];// 没走的记录为0
for (int i = 0; i < h; i++) {
String str = in.next();
in.nextLine();
a[i] = str.toCharArray();
for (int j = 0; j < l; j++) {
if (a[i][j] == '@') {// 记录出发点
startx = i;
starty = j;
}
}
}
book[startx][starty] = 1;// 标记出发点已走
sum = 1;
dfs(startx, starty);
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
static void dfs(int x, int y) {
int[][] next = { { 0, 1 }, { 1, 0 }, { 0, -1 }, { -1, 0 } };
int tx, ty;
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {// 计算下一点坐标
tx = x + next[i][0];
ty = y + next[i][1];
// 判断是否越界
if (tx < 0 || tx >= h || ty < 0 || ty >= l) {
continue;
}
if ((a[tx][ty] == '.' || a[tx][ty] == '@') && book[tx][ty] == 0) {// 可以往下走
book[tx][ty] = 1;// 标记已走
sum++;
// System.out.println(tx+" "+ty);
// for(int k=0;k<h;k++){
// for(int j=0;j<l;j++){
// System.out.print(book[k][j]);
// }
// System.out.println();
// }
dfs(tx, ty);
}
}
}
}
刷水题遇到,记录一下
多个空格替换为”.”
string=string.replaceAll(" +",".");
然后用”.”分割
String k[] = string.split(".");
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
public class Baoliuxiaoshu {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
double i=21.23456;
DecimalFormat test=new DecimalFormat(".000");
String tt=test.format(i);
System.out.println(i);
System.out.println(tt);
System.out.println(String.format("%.2f", i));
}
}
21.23456
21.235
21.23
操作环境:
Mac
Eclipse neon(4.6)
Tomcat 9
遇到的坑:
1. 安装TomcatPlugin报错 无法安装其插件
2. preferences中没有Server选项
3. Server中Runtime Environments没有tomcat9版本 无法配置
(导致jsp程序报错 not found on the Java Build Path)
解决方法:
- 安装TomcatPlugin报错 无法安装其插件
网上的方法是通过http://tomcatplugin.sf.net/update 来安装
可是事实上也可能是这个Eclipse的版本问题 我们在线安装等半天最后说不行 所以这里采取的最好的方法是通过离线安装
net.sf.eclipse.tomcat.updatesite-2016-09-21
(链接:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1pLLWefh 密码:20q8)
下载好压缩包后解压为文件夹,之后help-install new software-add-local-选择文件夹-然后安装就成功了
之后在preferences中可以找到tomcat 选择版本为9 选则tomcat的路径 配置完成
这时候工具栏就会出现tomcat的标志了
懒得上图了
- preferences中没有Server选项
还是像刚才一样help-install new software-地址栏输入 http://download.eclipse.org/releases/neon
然后下面那栏搜索JST(J2EE标准工具)下载
打开preferences就能看到Server选项了
如果不是这样安装或者用其他网上给的网址安装有可能出现下面这个问题
-
Server中Runtime Environments没有tomcat9版本 没法配置环境 结果导致jsp程序报错 not found on the Java Build Path
解决方法其实就是上面 一定要下载新版的插件才能出现tomcat9的选项
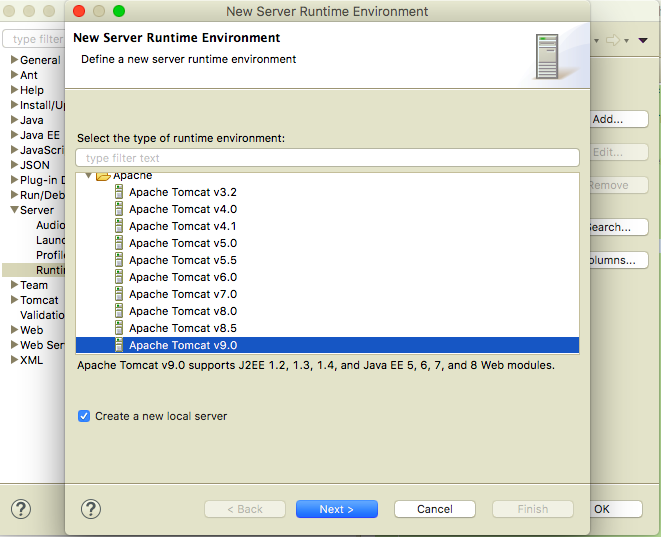
然后记得在创建web程序时选上配置好的这个runtime environments 就不报错啦
java中this常用有三种功能分别是:引用成员变量,调用构造方法,返回类实例。第一种功能比较容易理解,实际上也就是防止对象属性与方法中形参名相同。
哦对 顺便说下this的概念:this代表调用这个函数的对象。 其实和python中的self类似。
java中this调用构造方法
使用格式如下:
this([参数列表])
系统将根据参数列表来决定调用哪一个构造方法。使用this时还需注意下面几点:
- 用this调用构造方法时,该语句只能用在构造方法中。
- this语句必须是构造方法中的第一条语句。
- 和new不同,this虽然可以调用构造方法,但它只是执行构造方法中的语句,并不会创建对象。
(百度网友淡忘WHY66的回答)
举个例子
package cn.rui0;
public class Testhis {
public Testhis() {
this(911);//调用有参的构造方法 必须放在第一行
System.out.println("无参");
}
public Testhis(int i) {
System.out.println(i+"\n"+"有参");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Testhis a=new Testhis();//创建对象的同时会调用无参的构造方法
}
}
output:
911
有参
无参
好的,接下来说
java中this返回类实例
可以理解为返回类的对象,然后…要说的都在下面了..
package cn.rui0;
public class Testhis {
int i;
int num;
public Testhis() {
this(911);//必须放在第一行
num=100;
System.out.println("无参");
}
public Testhis(int i) {
this.i=i+1;
System.out.println(this.i+"\n"+"有参");
}
public Testhis aaa(){ //这里定义的返回值类型为Testhis这个类
num++;
return this;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Testhis a=new Testhis();//创建对象的同时会调用无参的构造方法
Testhis b=new Testhis();//创建另一个对比
System.out.println("*********************");
System.out.println(a);//输出实例化的类的对象a的地址
System.out.println(a.aaa());
/*
* 输出时运行了这个实例化的类的对象a中的方法aaa()
* 而方法aaa()中返回了当下调用这个方法的对象a(因为用的是this所以是当下调用这个方法的对象a,而不是b)
* 并且类型为Testhis,可以理解为又成为属于Testhis的一个对象,就是又有了Testhis类下的一波属性什么的
* 所以输出的地址和上面a的一样,并且可以进行像下面这样的输出
*/
System.out.println(b);//先对比一下输出地址 是不一样的对象 好了没它事了
System.out.println(a.aaa().getClass().getName ());//获取当前类名
System.out.println(a.num);//获取当前类实例化对象的属性
System.out.println(a.aaa().num);
// 这部分可能有点抽象,本辣鸡打字可能也没说太清,大家不懂可以再多去对比几次的输出的语句和output去理解
}
}
output:
912
有参
无参
912
有参
无参
*********************
cn.rui0.Testhis@7852e922
cn.rui0.Testhis@7852e922
cn.rui0.Testhis@4e25154f
cn.rui0.Testhis
102
103
注意:
被static修饰的方法没有this指针。因为被static修饰的方法是公共的,不能说属于哪个具体的对象的
感谢阅读,如果有错误非常欢迎指出~thx 🙂
如果在同一个包内可以不用import 直接创建对象 比如同包内有一个class内容为
package cn.rui0;
public class Telphone {
public Telphone() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
System.out.println("cn.rui0.Telphone");
}
}
直接这样 或者注释掉第二行都可以调用
package cn.rui0;
import cn.rui0.Telphone;
public class pagbao {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Telphone phone = new Telphone();
}
}
但如果还有个包或者子包,他们和上面那个包中有相同的类名时
package cn.rui0.cs;
public class Telphone {
public Telphone() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
System.out.println("cn.rui0.cs.Telphone");
}
}
调用时就需要
import cn.rui0.cs.Telphone;
才能输出 cn.rui0.cs.Telphone
如果你像下面这样调用 没有明确指明具体是哪个class
package cn.rui0;
import cn.rui0.cs.*;//或者调用其他包时没有指明文件
public class pagbao {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Telphone phone = new Telphone();
}
}
则他会首先寻找自己包内有没有这个类,如果有就先调用自己包里的最后输出cn.rui0.Telphone 执行过程就如第一个一样。(如果没有就再调用import了的.cs里的这个类 最后输出的就是cn.rui0.cs.Telphone)像上面这个咱们2已经假设了两个包内有相同的类名的情况,它当然就会输出cn.rui0.Telphone了
so,
如果要调用的类在另一个包或者子包并与这个包中的类名不同,则可以用通配符调用其所有文件或者还是指定文件调用 如下
另一个包中的tclass类
package cn.ruilin;
public class tclass {
public tclass() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
System.out.println("cn.ruilin.tclass");
}
}
调用该包内其全部文件
package cn.rui0;
import cn.ruilin.*;
public class pagbao {
public static void main(String[] args) {
tclass phone = new tclass();
}
}
这样是可以运行的 并且输出cn.ruilin.tclass
也就是说,你不导入包时程序会自动把本包下的文件导入提供调用,当然你也可以指明调用哪个。
而当导入其他包的类与本包类重名时,不能采用import 包名.*;此时java程序只承认本包下的文件;而应该采用import 包名.文件名,此时java程序只承认由其他包导入的文件。
初学者可能会搞晕或者是不理解,个人认为要理解并区分方法与构造方法 我们首先应该了解他们的作用,用作用做对比才能方便区分,接下来才是慢慢了解如何使用。
首先先简单了解一下大概作用
- 方法: 方法是语句的集合,它们在一起执行一个功能。实际上就相当于python或者c中的函数。
- 构造方法: 构造方法其实就是对类进行里面数据的初始化定义,它是方法中的一种(方法分为三种,接下来会说到),你可以有也可以没有。没有系统会自动给你生成一个无参的。重点也是需要提前强调的是它需要与类名相同。
之后继续说
- 方法: 一个类中的方法分为三类: 1)全局方法 2) 成员方法 3)构造方法
public class Test{
private int xxx;
public Test(int age){ //这是构造方法
xxxxxx
}
public void xxxxxx(int xxxx){ //这是成员方法
xxxxxx
}
public static int xxxxx(){ //这是全局方法,加了static ,成员方法就会变成全局方法
return xxxxx;
}
}
三者区别:
- 成员方法必须构造类的实例化对象进行访问
- 全局方法可以用类直接访问
- 构造方法是实例化对象时进行初始化的
一般情况下,定义一个方法包含以下语法:
修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(参数类型 参数名){
...
方法体
...
return 返回值;
}
- 修饰符:修饰符,这是可选的,告诉编译器如何调用该方法。定义了该方法的访问类型。
- 返回值类型 :方法可能会返回值。returnValueType 是方法返回值的数据类型。有些方法执行所需的操作,但没有返回值。在这种情况下,returnValueType 是关键字void。
- 方法名:是方法的实际名称。方法名和参数表共同构成方法签名。
- 参数类型:参数像是一个占位符。当方法被调用时,传递值给参数。这个值被称为实参或变量。参数列表是指方法的参数类型、顺序和参数的个数。参数是可选的,方法可以不包含任何参数。
- 方法体:方法体包含具体的语句,定义该方法的功能。
在创建对象的时候,对象成员可以由构造函数方法进行初始化。
也就是我们创造实例化的代码中 new后面跟的就是构造方法
Telphone phone=new Telphone();
等号右面
new Telphone()
相当于是以Telphone类为模板,在堆空间里创建一个Telphone类对象
末尾的()代表着,在对象创建后,立即调用Telphone类的构造函数,对刚生成的对象进行初始化。
等号左面
Telphone phone
创建命名了一个Telphone类引用变量phone
这里用一下imooc的图
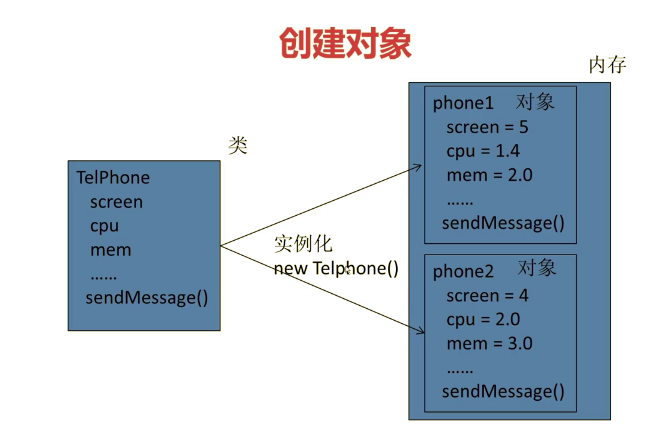
接下来再说下有参和无参的构造方法的区别
有参就是你可以在创建对象时候赋值
public Test(String name){
mz=name;
}
Test为构造方法(函数)名 需要与类名相同
创建对象
Test name=new Test("xxxxx");
无参就需要这样
public Test(){
}
public String mingzi(String name){
mz=name;
return mz;
}
创建对象并赋值
Test nick=new Test();
nick.mingzi="ruilin";
总的来说,有参构造函数和无参构造函数都可以提前初始化一些值,但是有参可以在实例化时就进行赋值而无参不可以。这些赋值或者说初始化都是为了后面调用方法(函数)更加方便或者是去提供一些功能所必要的参数来防止报错,这也就是构造方法的作用。
最后再放一个有参的构造方法的例子便于理解
public class Testff {
int num;
public Testff(int n){
num = n;
}
public int numb(int a,int b){
System.out.println(a+"\n"+b+"\n"+num);
int c=a+b+num;
return c;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Testff test=new Testff(11);
System.out.println(test.num+"\n"+"---------");
System.out.println(test.numb(1,2));
}
}
output:
11
---------
1
2
11
14
以上就是我对java中方法与构造方法的理解与区分,其中也简述了对有参与无参构造方法的一些理解,欢迎交流。
了解桶排序
这个算法就好比有 11 个桶,编号从 0~10。每出现一个数,就在对应编号的桶中放一个 小旗子,最后只要数数每个桶中有几个小旗子就 OK 了。例如 2 号桶中有 1 个小旗子,表示 2 出现了一次;3 号桶中有 1 个小旗子,表示 3 出现了一次;5 号桶中有 2 个小旗子,表示 5 出现了两次;8 号桶中有 1 个小旗子,表示 8 出现了一次。

如何实现桶排序
- 使用数组代替桶的作用,利用数组的下标直接排好顺序
- 每次遇到相应的旗子编号就对其对应的桶即相同的数组下标如a[5]的值+1用于记录出现几次
- 依次判断桶中的值即为输出的次数
- 依次按照次数输出桶的编号即数组的下标
利用java实现
题目:
考试成绩需要由小往大依次排序 成绩范围为0-10 学生数为5人 请依次输入学生成绩并进行排序
java code:
import java.util.Scanner;;
public class sortest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] scores=new int[11];//定义一个空间大小为11的变量 0-10即11个
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);//控制台等待输入
for(int i=0;i<=10;i++){ //初始化scores值为0
scores[i]=0;
}
for(int j=1;j<=5;j++){ //循环输入5名学生成绩
System.out.println("请输入第"+j+"名学生成绩");
int t=input.nextInt();
scores[t]++;//计数
}
System.out.println("**************");
for(int a=0;a<=10;a++){ //依次判断每个成绩
for(int b=1;b<=scores[a];b++){ //依次判断每个成绩的人数
System.out.println(a);
}
}
}
}



